Build your own custom destination using a serverless function
Overview
This destination invokes an AWS Lambda function whenever data changes in your model. It makes it possible to build your own custom integrations that execute code written in Python, Java, Go, PowerShell, Node.js, C#, or Ruby.
This destination was designed to be as flexible as possible. You can exercise granular control over function triggers, batching, rate limits, concurrency limits, and even error handling. Together, these features let you integrate Hightouch with any internal tool or third-party API.
Under the hood, the AWS Lambda destination uses Hightouch's powerful sync engine, so you continue to benefit from the security and observability features available in our native SaaS destinations.
Example use cases include:
- Syncing data to web APIs not yet natively supported
- Enriching data using external sources like Clearbit and ZoomInfo
- Transforming and filtering data using code instead of SQL
Getting started
Connect to your AWS account
When setting up the AWS Lambda destination for the first time, you need to enter your AWS Credentials to give Hightouch access to your AWS account. Hightouch needs permission to invoke Lambda functions on your behalf.
Hightouch believes in the principle of least privilege. We ask for no more permissions than absolutely necessary. For the AWS Lambda destination, Hightouch requires lambda:InvokeFunction for the specific function or functions you want to invoke.
When configuring your credentials in Hightouch, you have two options:
- Setting up a cross-account role (recommended)
- Providing an access key
Set up cross-account role
Cross-account roles are the most secure method for granting Hightouch access to specific Lambda functions in your AWS account.
You need the Account ID and External ID in the Hightouch UI to set up a cross-account role.
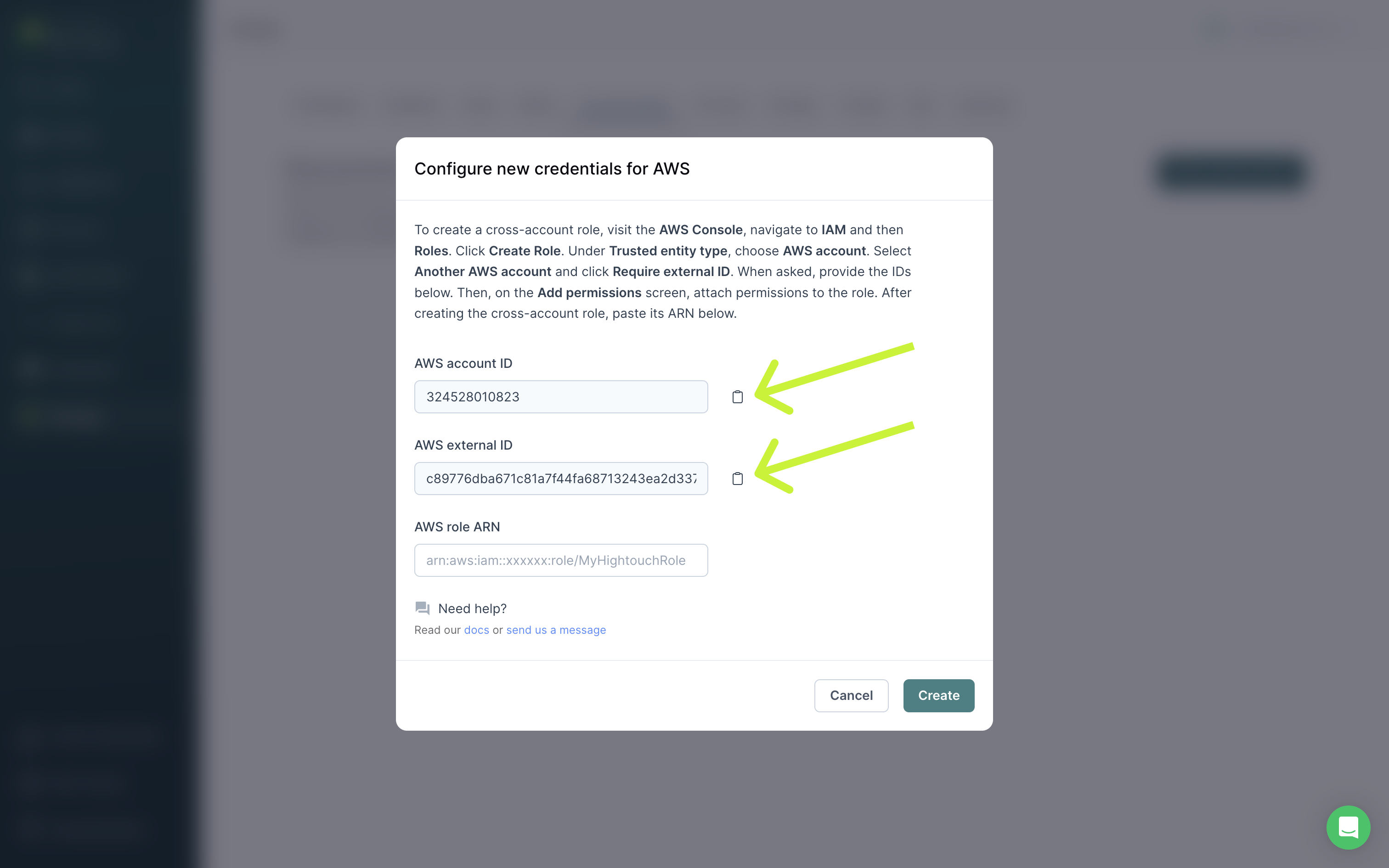
- In the AWS Console, navigate to IAM → Roles.
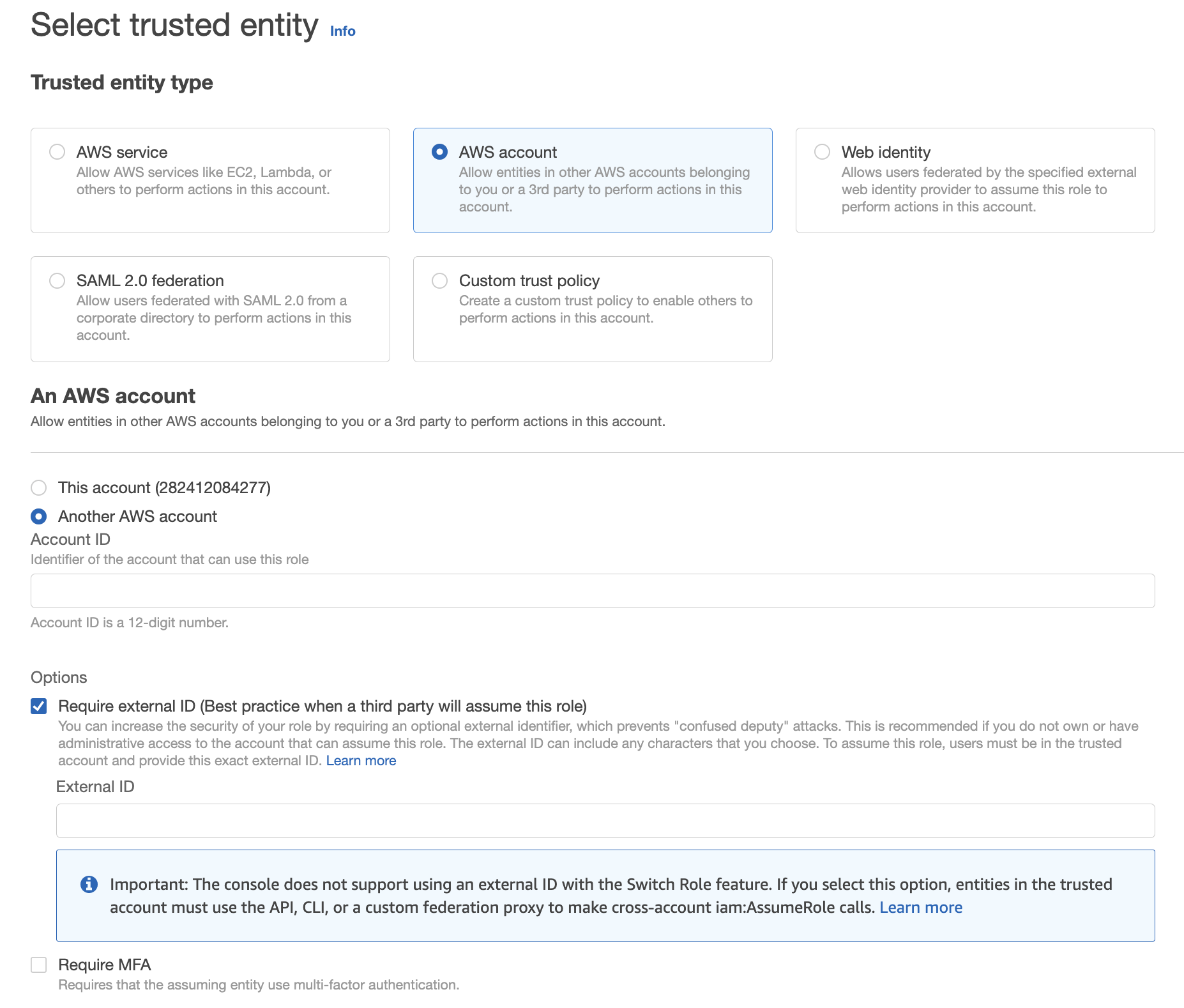
- Click Create Role.
- Under Trusted entity type, choose AWS account.
- Select Another AWS account and also click Require external ID.
- Copy/paste the Account ID from Hightouch into the Account ID field in AWS.
- Copy/paste the External ID from Hightouch into the External ID field in AWS.
- On the Add permissions screen, proceed to attach permissions to the role using any policy that includes at least
lambda:InvokeFunction. Then create the role.
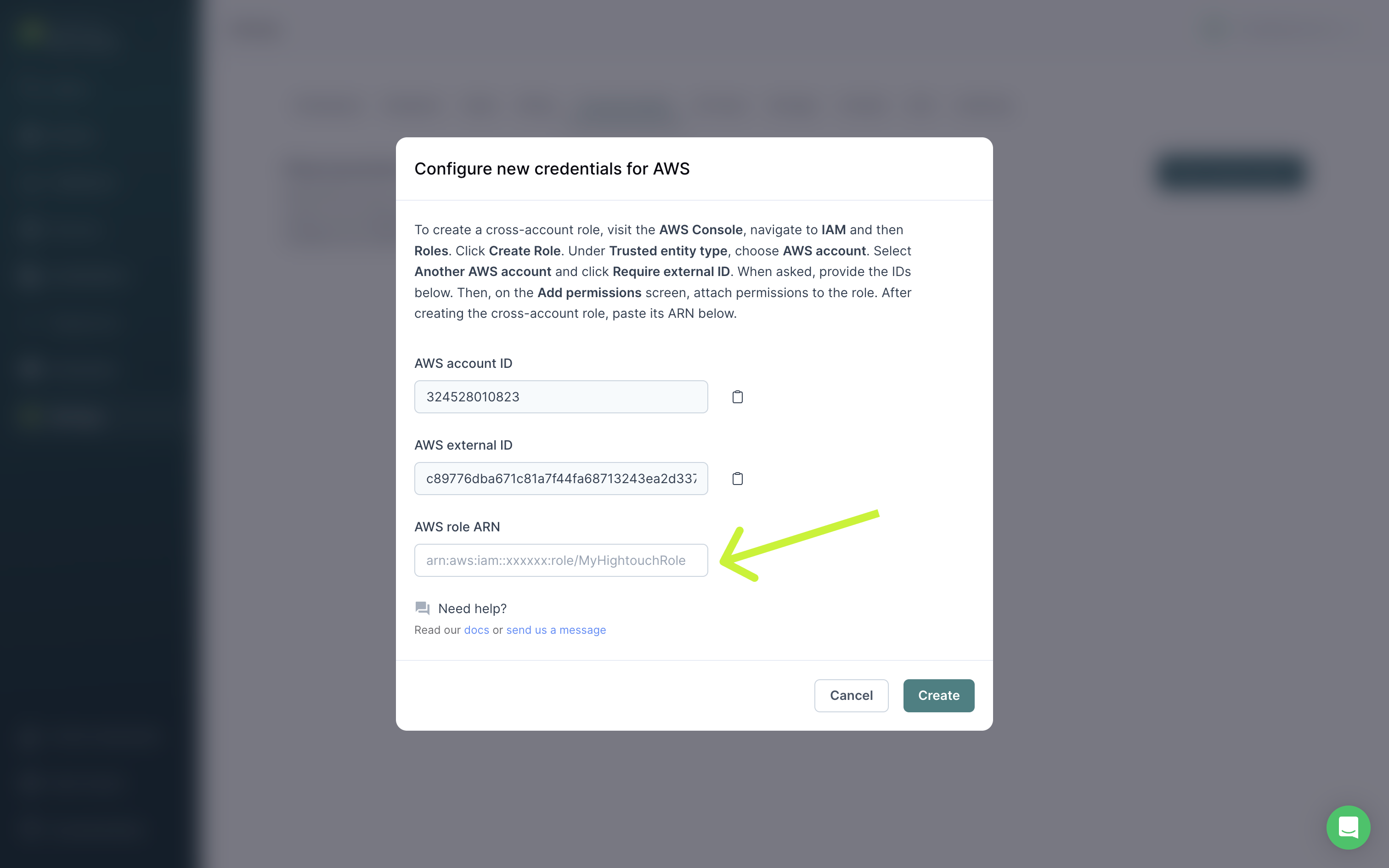
- Copy/paste the Role ARN from AWS into Hightouch. Click Create to finish setting up your cross-account role.
Provide access key
If you don't want to create a cross-account role, you can create a regular IAM user and share a Access Key ID and Secret Access Key with Hightouch.
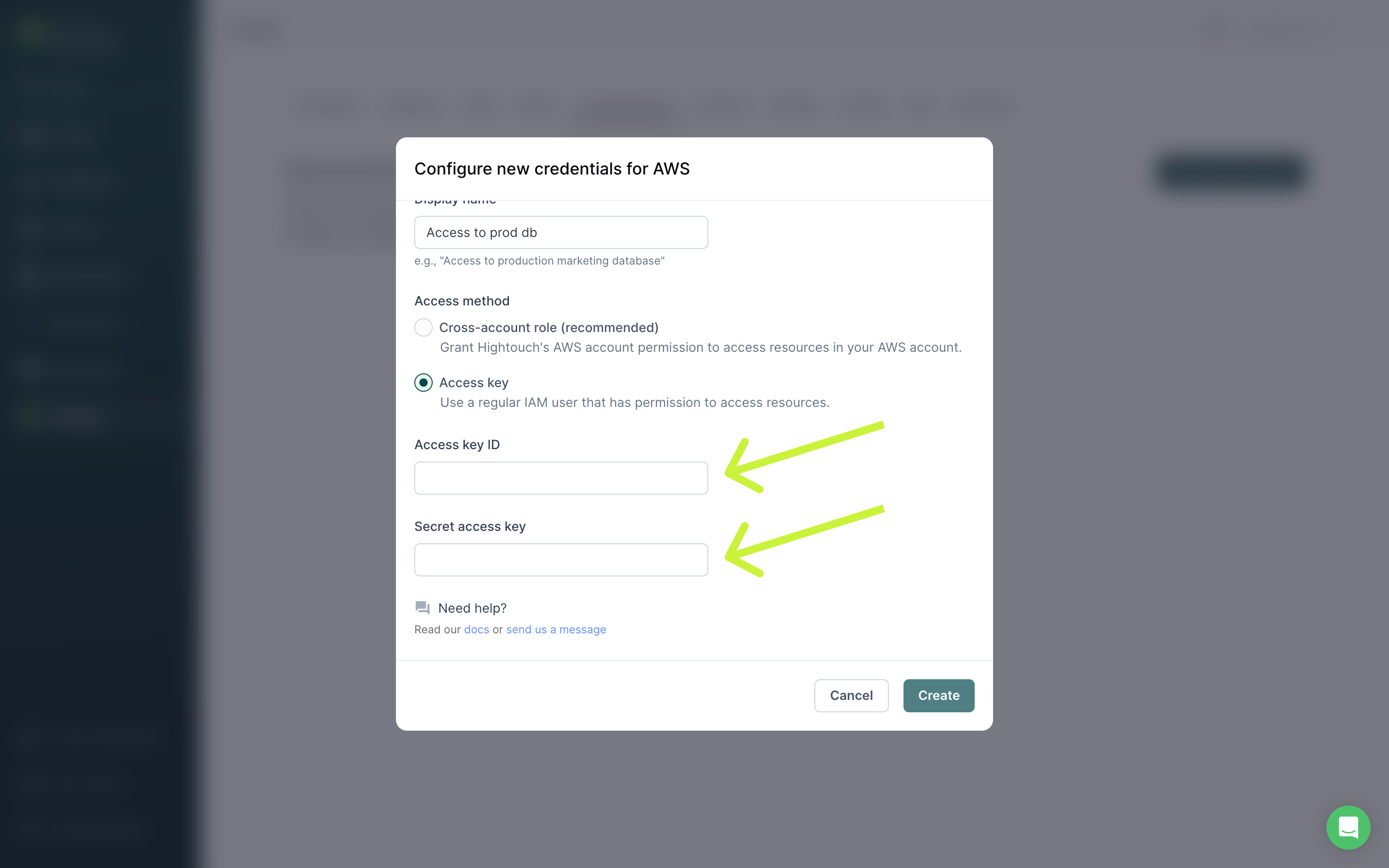
Be sure to attach the user to a permission policy that includes lambda:InvokeFunction for the specific function or functions you want to invoke via a Hightouch sync.
An example policy looks like this:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["lambda:InvokeFunction"],
"Resource": [
"YOUR_LAMBDA_ARN_1",
"YOUR_LAMBDA_ARN_2",
"YOUR_LAMBDA_ARN_3"
]
}
]
}
Syncing data
Once you've authenticated your AWS account in Hightouch, you've completed setup for a Lambda destination in your Hightouch workspace. The next step is to configure a sync that invokes your function whenever rows are added, changed, or removed in your model.
Specify your Lambda function
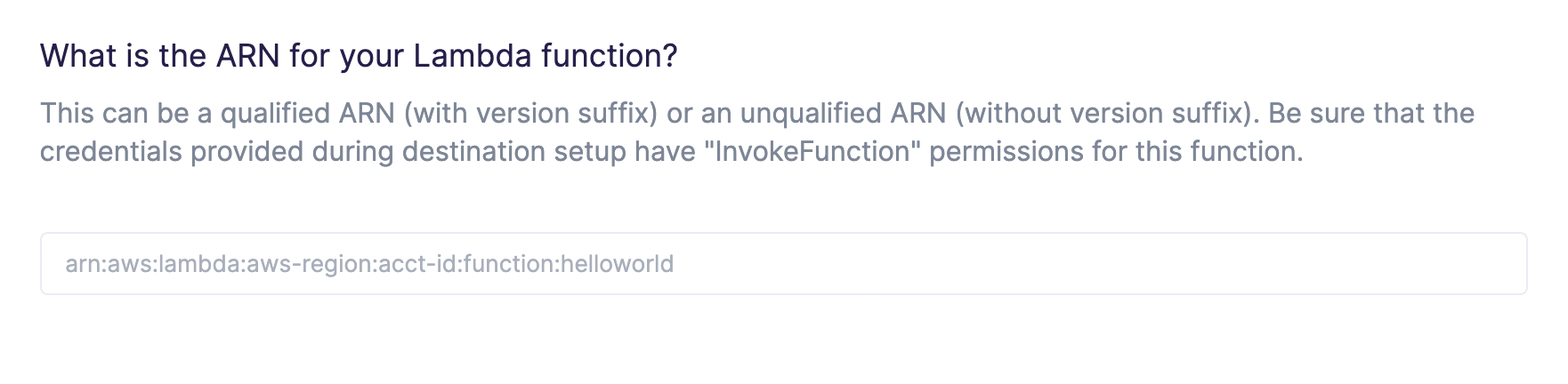
To get started, you need the ARN of the Lambda function you want to invoke. You can find the ARN in the AWS web console.
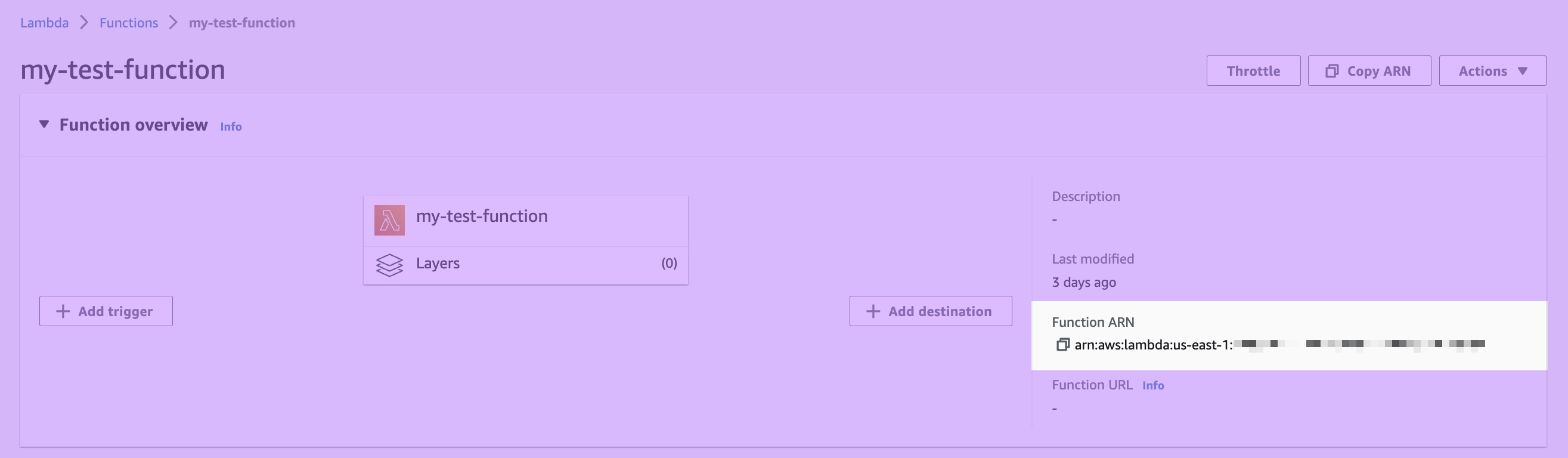
When providing an ARN, you can use either a qualified ARN or an unqualified ARN. A qualified ARN has a version suffix, for example, arn:aws:lambda:aws-region:acct-id:function:helloworld:42. Unqualified ARNs don't have a version suffix, for example, arn:aws:lambda:aws-region:acct-id:function:helloworld.
Enter your ARN into your sync configuration in Hightouch.
Choose your function triggers
Hightouch monitors your data model for added, changed, and/or removed rows. In this step, you specify which of these events should invoke your function.

Suppose you want to use AWS Lambda to send a confirmation email whenever a customer places a new order or updates an existing order. Your model might look something like SELECT * FROM orders. The Lambda function should be triggered whenever rows are added—for example, when customers place new orders—or whenever rows change—when orders are updated. Therefore, you would want to enable the Rows added and Rows changed triggers. When invoking your function, Hightouch passes along metadata about why the function was invoked.
All function invocations are synchronous, meaning that Hightouch invokes your Lambda function and waits for its response.
Configure initial sync behavior
In this step, you tell Hightouch how to handle rows present in your model results during the first sync run.
Certain workflows, such as hydrating a CRM for the first time, may require performing a backfill of all rows during the initial sync. For other use cases, such as sending confirmation emails, you might only want to invoke your function in response to future data changes.

Configure batch size
By default, Hightouch separately invokes your Lambda function for each added, changed, or removed row.
Certain high-throughput use cases may require batching together multiple rows in the payload. Hightouch supports batches of up to 1000 rows per function invocation.
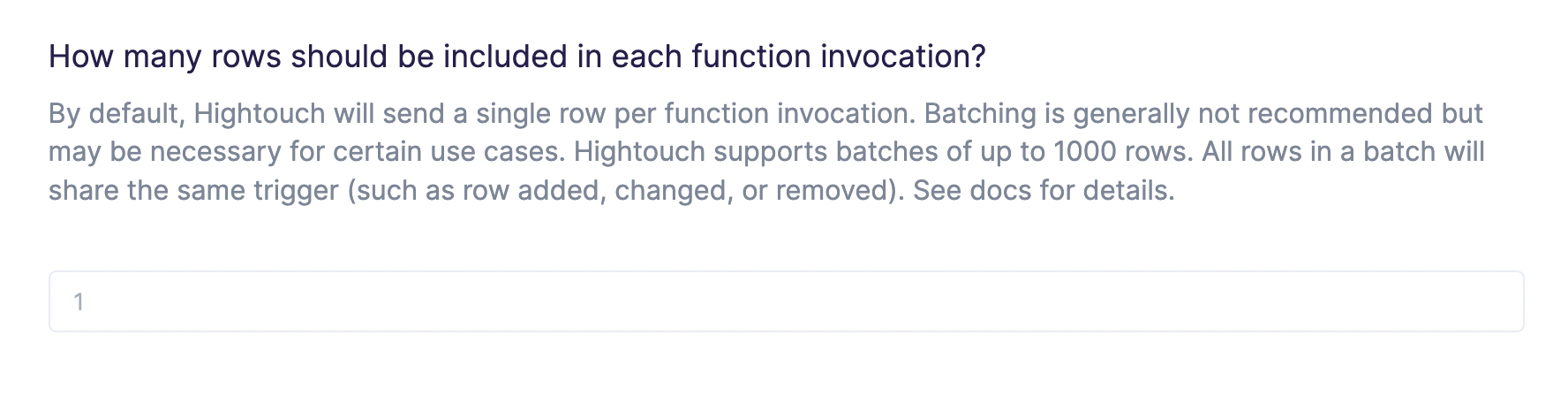
Batching isn't recommended unless absolutely necessary for performance reasons. Enabling this feature requires your Lambda function to be either idempotent or significantly more fault tolerant in the event of a partial batch failure.
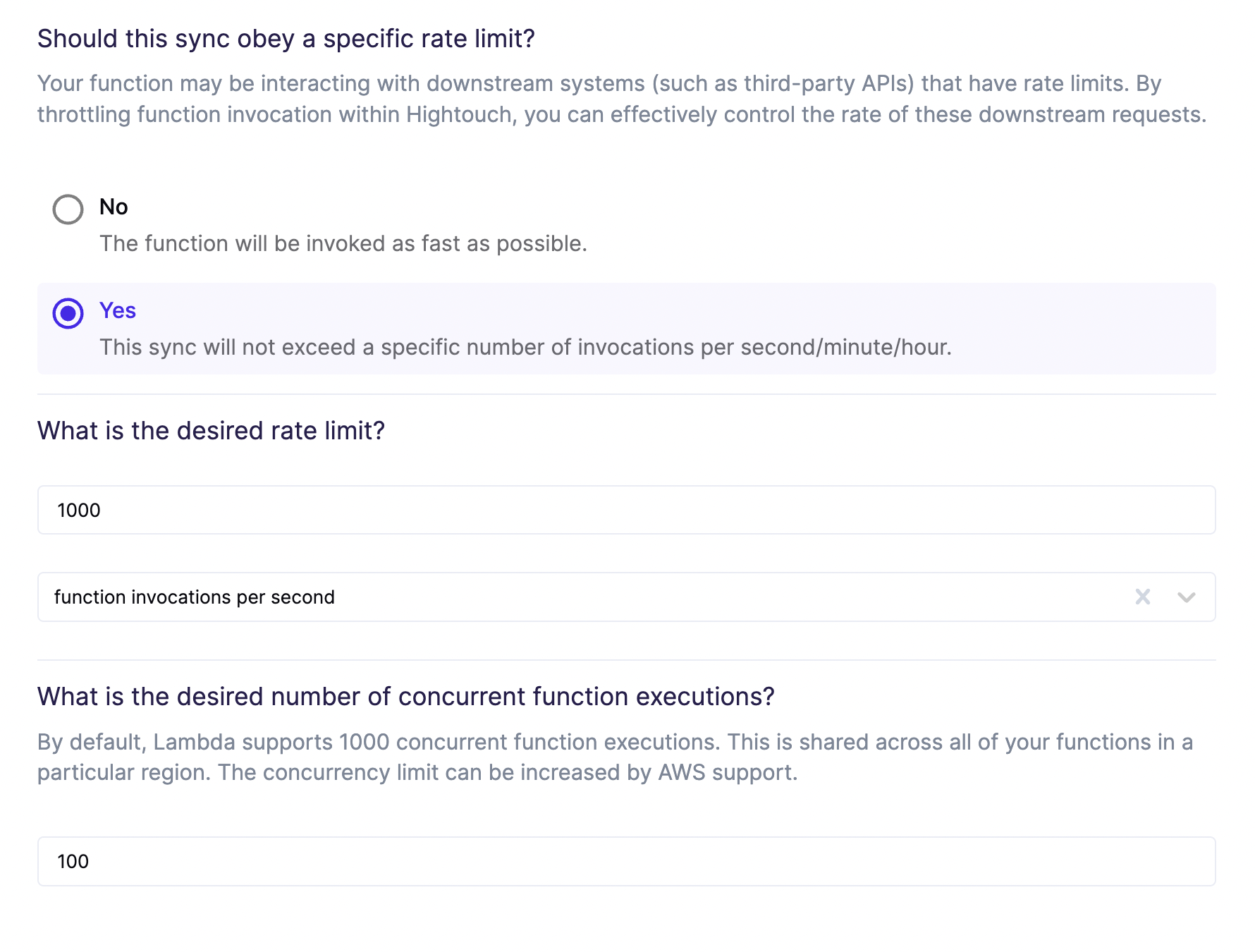
Configure rate and concurrency limits
In this step, you declare whether function invocations should be throttled.
To determine the ideal limits, you should consider whether your function interacts with any downstream services that have limits of their own.
Most modern web APIs enforce rate limits, which set a maximum allowed number of requests per second, minute, or hour. Occasionally, APIs may also have concurrency limits, which set a maximum allowed number of requests that can be processed simultaneously. Rate limits and concurrency limits both affect overall sync speed.
Configure error handling
Lambda functions can fail for many reasons. Hightouch's retry logic for this destination doesn't discriminate between invocation errors, for example, missing permissions, runtime errors, for example, due to syntax issues, or function errors, for example, due to uncaught exceptions. Hightouch retries all errors eventually.
In this step, you decide whether errors should be retried immediately or during the next sync run. If you choose to retry immediately, you can specify how many retries should be attempted during the sync run. If all these retries fail, Hightouch retires the request during subsequent sync runs until it succeeds.
If an error is gracefully caught in your function, you can flag it as a rejected row and provide a custom error message using the response format specified in the error handling section.
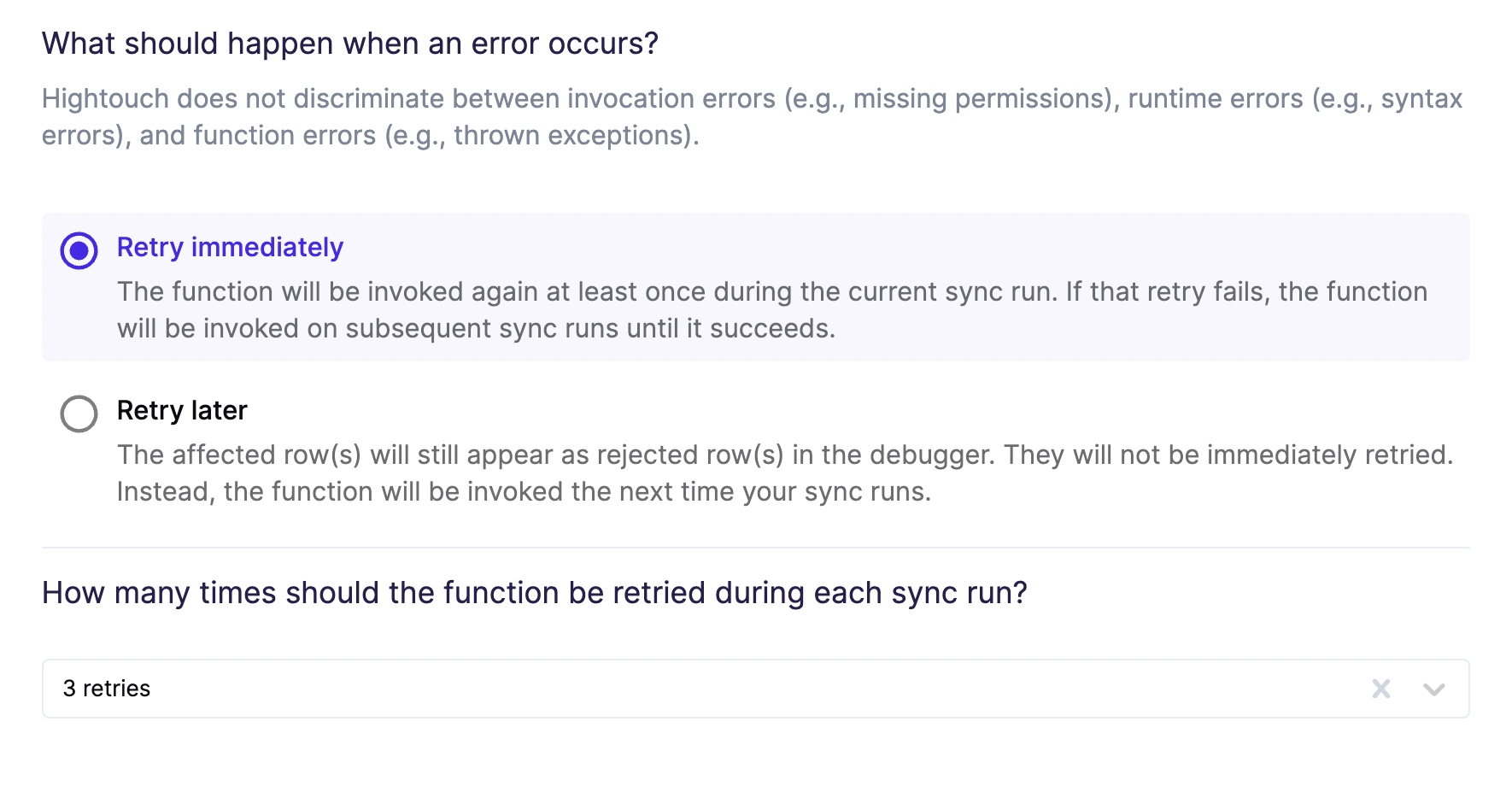
You can also include retry logic inside of your Lambda function. After exhausting all retry attempts during a function invocation, respond with an error so that Hightouch knows to reinvoke the function later.
Invocation payload schema
The payload, also known as the "event document," contains your row data in JSON format, along with additional metadata. When writing your Lambda function, you can assume that all function invocations include a payload following this schema:
{
"operation": XXXXX,
"primary_key_column": XXXXX,
"rows": [
{
XXXXXX
}
],
"metadata": {
"api_version": XXXXX,
"sync_id": XXXXX,
"sync_run_id": XXXXX
}
}
Invocation payload properties
operation
The row operation, also known as the trigger, explains why your function was invoked.
Its possible values are these strings: "add", "change", and "remove".
primary_key_column
This string refers to the column name of the primary key for your Hightouch model.
rows
This is an array of objects, with each object containing row data from your Hightouch model.
metadata
This is an object containing three key/value pairs:
api_version(integer): currently set to1, this identifier only changes if the payload schema is modified in the futuresync_id(integer): this is the unique identifier for the Hightouch sync configuration associated with the function invocationsync_run_id(integer): this is the unique identifier for the specific sync run associated with the function invocation
Example invocation payload
Suppose a new row is added to your model:
customer_id | email_address | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 928713 | john.doe@example.com | John | Doe |
The payload for the function invocation would look like this:
{
"operation": "add",
"primary_key_column": "customer_id",
"rows": [
{
"customer_id": "928713",
"email": "john.doe@example.com",
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe"
}
],
"metadata": {
"api_version": 1,
"sync_id": XXXXX,
"sync_run_id": XXXXX
}
}
Note that rows is an array containing a single element.
Example invocation payload for batching
Suppose three new rows are added to your model:
customer_id | email_address | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 928713 | alice.doe@example.com | Alice | Doe |
| 283743 | bob.doe@example.com | Bob | Doe |
| 162352 | carol.doe@example.com | Carol | Doe |
The payload for the function invocation would look like this:
{
"operation": "add",
"primary_key_column": "customer_id",
"rows": [
{
"customer_id": "928713",
"email": "alice.doe@example.com",
"first_name": "Alice",
"last_name": "Doe"
},
{
"customer_id": "283743",
"email": "bob.doe@example.com",
"first_name": "Bob",
"last_name": "Doe"
},
{
"customer_id": "162352",
"email": "carol.doe@example.com",
"first_name": "Carol",
"last_name": "Doe"
}
],
"metadata": {
"api_version": 1,
"sync_id": XXXXX,
"sync_run_id": XXXXX
}
}
When batching is enabled, rows sharing a common operation type—add, change, remove: are batched together. Function invocations always represent exactly one operation type.
Response payload schema
If your Lambda function fails to process any rows, it can respond with an array of "rejected rows" that encountered errors. Each rejected row should be identified by its primary key/value and may be associated with an optional error message. Hightouch retries these rows.
If there is an error, the response payload looks like this:
{
"errors": [
{
"primary_key_value": XXXXX,
"reason": XXXXX
}
]
}
Response payload properties
Errors in the errors array have these properties:
primary_key_value
This identifies the rejected row that needs to be retried.
reason (optional)
This string may represent an error message or any other information that would be helpful for debugging and monitoring sync health.
Example success response payload
If all rows are processed successfully, your function responds with an empty payload.
{}
Example response payload for rejected rows
Suppose three new rows are added to your model:
customer_id | email_address | first_name | last_name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 928713 | alice.doe@example.com | Alice | Doe |
| 283743 | bob.doe@example.com | Bob | Doe |
| 162352 | carol.doe@example.com | Carol | Doe |
While processing these rows, your Lambda function encounters two errors:
- Alice's email can't be found in the downstream service
- Bob's email already exists in the downstream service
To surface these errors in Hightouch, your function should respond like this:
{
"errors": [
{
"primary_key_value": "928713",
"reason": "Email not found"
},
{
"primary_key_value": "283743",
"reason": "Email already exists"
}
]
}
The primary key values (928713 and 283743) refer to customer_id values. The customer_id column was designated the primary_key_column in the function invocation payload.
Example response payload for other errors
If your function experiences an invocation error, for example, exceeding AWS Lambda rate limits, runtime error, for example, due to syntax issues, or function error, for example, due to uncaught exceptions, all rows in the batch are automatically marked as rejected rows.
Tips and troubleshooting
Common errors
To date, our customers haven't experienced any errors while using this destination. If you run into any issues, please don't hesitate to . We're here to help.
Live debugger
Hightouch provides complete visibility into the API calls made during each of your sync runs. We recommend reading our article on debugging tips and tricks to learn more.
Sync alerts
Hightouch can alert you of sync issues via Slack, PagerDuty, SMS, or email. For details, please visit our article on alerting.
