What is a customer data warehouse?
Find out what a customer data warehouse is and how it can turn insights into action.
Craig Dennis
April 4, 2023
|10 minutes

For years, companies have relied on data warehouses to store, manipulate, and analyze data. While many organizations have solved the problem of getting data into the warehouse, leveraging those right insights to drive action is a key challenge.
In this article, you’ll learn what a customer data warehouse is, the core use cases they address, and the tools needed to build one.
What is a Customer Data Warehouse?
A customer data warehouse is a centralized platform to analyze, segment, and activate all of your customer data. The entire purpose of a customer data warehouse is to help you send enriched data to marketing destinations like ad platforms or lifecycle marketing tools.
Traditional data warehouses focus on ingesting data into the platform so your data team can model and transform it for analytics use cases. Usually, this means persisting this data to a dashboard or report for your internal stakeholders to consume.
A customer data warehouse completely flips this paradigm. The focus is on taking the rich insights your data team has unlocked in your warehouse and making that information available to your other business teams in the native tools they use daily.
Previously, data warehouses were only accessible to technical users who knew how to write SQL. However, this is no longer the case with the introduction of the Composable CDP and Reverse ETL. With a customer data warehouse, any user (regardless of technical skill) can visually define and segment audiences for activation using Customer Studio.
CDWs vs. CDPs
At first glance, you might think a customer data warehouse is identical to a customer data platform (CDP). They both store customer data and offer solutions for activating data. However, there’s a core difference between the two. Customer data warehouses have access to all your data across all your sources, creating a single coherent customer record. Conversely, most CDPs only collect clickstream and behavioral event data (pages viewed, items added to cart, last login date, etc.) from within your product.
You often capture these customer events using a proprietary SDK (software development kit) via a snippet of code embedded in your app or website. Only collecting clickstream and behavioral data means you're missing critical data from your other first-party data sources across sales, marketing, finance, support, etc.
Additionally, CDPs operate as their own separate entity in parallel to your warehouse, which means they come with a high investment cost and lengthy implementation/onboarding times. Not to mention the fact that they make you pay for an additional layer of data storage even though that same data already exists in your data warehouse in the first place.
Customer data warehouses are much more flexible compared to CDPs because they don’t limit you on how you manage your data. You have complete control over how it’s structured and modeled.
Because CDPs focus solely on activation use cases, they restrict how long you can store historical data. In most cases, all of your data must be tied to a strict user/account model structure.
The core difference between a customer data warehouse and a CDP is that a customer data warehouse builds on top of your existing data infrastructure, and CDP forces you to purchase another tool that doesn’t necessarily integrate into your current technology stack.
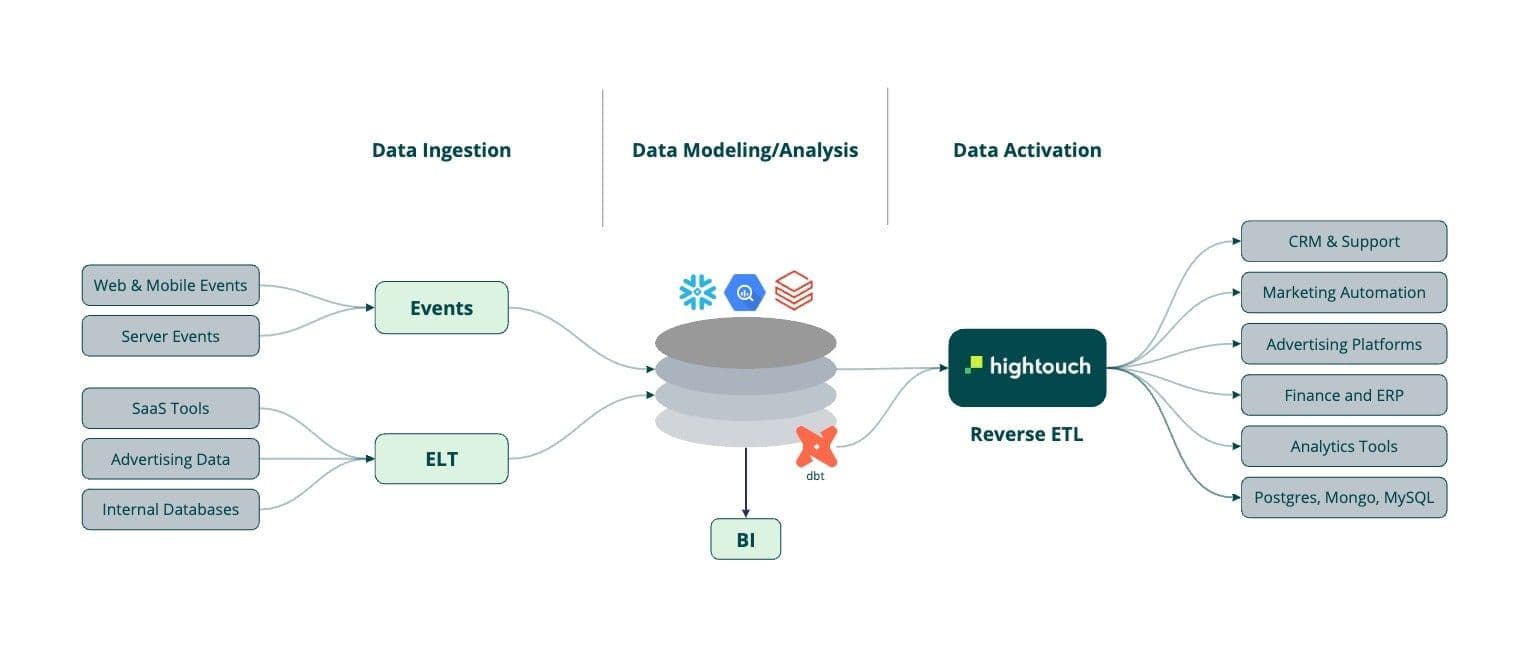
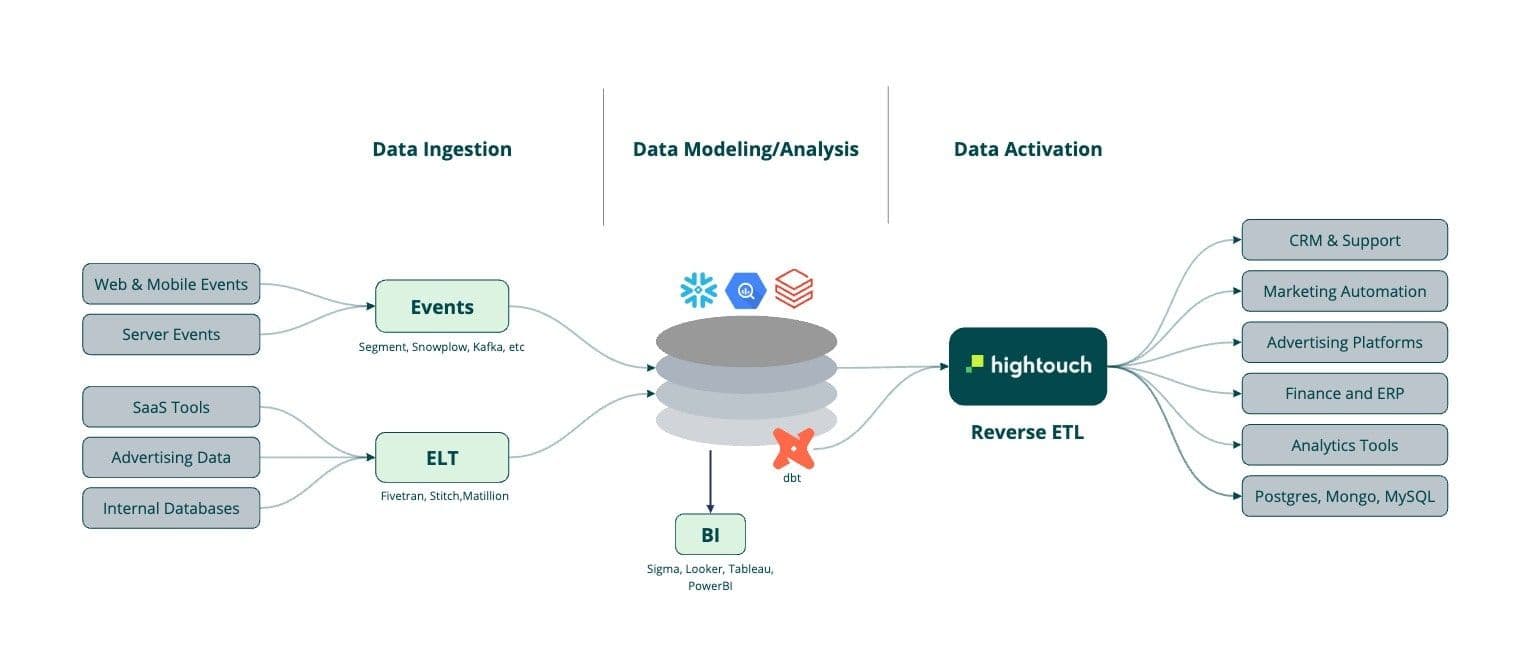
Customer Data Warehouse Architecture
A customer data warehouse relies on a handful of components to achieve the outcome it’s set out to do. The three main components are data ingestion, data modeling, and data activation.
- Data collection: Data collection is the act of moving data across multiple sources and loading it into a single location. You can use a tool to help collect and ingest behavioral data. To collect and ingest non-event stream data from your SaaS tools or your organization databases, you can use an ELT solution to save you from building an in-house solution.
- Data modeling: Data modeling helps to produce data into tables and views by transforming and modeling your data. Data modeling tools allow data teams to version, test, and document data models before they are deployed to production with monitoring and visibility.
- Data activation: Data activation lets you sync your data from your data warehouse to your business tools like Salesforce, Iterable, Facebook Ads, or Braze. Doing so lets your business teams have access to enriched data to help them perform their goal better. And better data to create personalized marketing campaigns.
Customer Data Warehouse Use Cases
Moving the rich customer data out of your warehouse unlocks additional use cases outside of analytics that can have huge implications for your marketing teams.
Lifecycle Marketing
Sending customer data to your lifecycle marketing tools can unlock huge value for marketing teams. With lifecycle marketing, you can keep your customers engaged throughout every stage of your marketing funnel, so new customers are more likely to convert, and existing customers are more likely to stay loyal.
A customer data warehouse can help you build customized audiences for your marketing channels, whether email, push notifications, or SMS messages. It gives you a centralized platform to orchestrate your omnichannel experiences and create multi-threaded campaigns.
Retargeting
Retargeting customers with ads is a critical use case for many companies. It’s unrealistic to think that every customer who lands on your website will buy or sign up for your product. They may not have time to buy, they might not trust who you are, or they might not truly understand the value of your product.
For example, simply by sending a list of shopping cart abandoners to Google Ads, you can retarget these users with ads for the products they were interested in. Alternatively, if you want to optimize your ad spend, you could send an exclusion list to Google so you don’t accidentally target users who already purchased from you in the first place. In both scenarios, you can optimize for CAC (customer acquisition cost) and ROAS (return on ad spend.)
Lookalike Audiences
Another great way to optimize your ad spend is simply by uploading existing customer audience lists to your ad platforms. Doing this can help platforms like Google and Facebook better surface your ads to people who align with your ideal customer profile or ICP, leading to higher conversions and more ROAS.
Data Enrichment
Another advantage of a customer data warehouse is that it enriches your operational tools with a holistic view of your customer. Every SaaS tool or database shows a slightly different view of the customer. For example, Salesforce has different data than Marketo, and Zendesk has different data than Netsuite. However, a customer data warehouse has all this information, allowing you to enrich your operational tools with this relevant customer data.
With a customer data warehouse, you can provide enriched data to your various business teams in the tools they use every day. Here are a few use-case examples of what this might look like in practice:
- Sending product usage data (e.g., last login date, active users, workspace created) to Salesforce so your sales reps can monitor account activity
- Uploading churn scores to Zendesk so your support teams can proactively take action before customers churn
On-site Personalization
Customer data warehouses can also power on-site personalization. Having access to all of your customer data (both first-party and third-party) means you can upload core attributes to your production databases so your product team can create personalized experiences for specific audiences and user preferences.
For example, you could showcase specific products or information to certain audiences or users based on their browsing/purchase history. Uploading enriched customer data to your production database achieves higher engagement and conversion rates with your users.
Automation
While a customer data warehouse can power many different business use cases, the main value often is automation. Rather than forcing your business teams to make ad-hoc requests whenever they need a dataset or audience, you can set up automated data syncs to your downstream applications via Reverse ETL.
Having access to this data allows your data team to focus on optimizing your infrastructure and unlocking new insights–and it enables your business teams to have access to the data they need when they need it.
Customer Data Warehouse Tools
There are some key tools needed to achieve a customer data warehouse. You need a tool for storage, data integration, data modeling, and data activation. Below are some of the most popular customer data warehouse tools for each task.
Fivetran
Fivetran is your go-to data integration solution for extracting and ingesting data into your warehouse. Fivetran connects to your various data sources and transfers that data into your data warehouse. Fivetran manages these pipelines so your data team doesn’t have to build and maintain their own ETL pipelines. Fivetran allows you to set sync frequency as small as five minutes and can even offer data streaming so you can be confident the data in your warehouse is up to date.
Snowflake
Snowflake is one of the popular data warehouse tools. Snowflake provides the perfect location for storing all your customer data in one location, so you have that data available for data analysis and data activation.
Snowflake manages the administration and maintenance of your data warehouse, allowing flexibility in how you structure your data, and includes features such as auto-scaling, which automatically starts and stops clusters based on usage.
dbt
dbt is one of the most popular tools for data transformation and modeling. It integrates with a wide range of cloud data platforms and is powered by SQL. dbt lets you write, orchestrate, and manage SQL scripts and has features such as automated testing, documentation, and lineage graphs to help streamline the transformation process.
Hightouch
Hightouch is the leading industry data activation tool. It enables you to take those insights and send that data directly into the downstream tools by using a technology called Reverse ETL. Like the use cases of data activation mentioned above, it allows for better-built customer segmentation which powers personalized marketing campaigns.
Hightouch also offers a no-code solution for audience building as part of the Customer Studio, enabling marketers to take control over the data they need.
Final Thoughts
Customer data warehouses are essential if you want to take action on your data, whereas you use a traditional data warehouse for analytics. You need a combination of both to really help drive your business forward.
If your data is dormant in your data warehouse, you’ve effectively just gone from multiple data silos to one big one. This is why a customer data warehouse enables you to take the rich insights uncovered within your data warehouse and get them into the hands of your business team to help them drive their business outcomes.










